Stereocephalus tutus, Lambe, 1902
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.3233762 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4583897 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03BAEA64-B52E-4055-70E0-FD09FA33D990 |
|
treatment provided by |
Jeremy |
|
scientific name |
Stereocephalus tutus |
| status |
|
Stereocephalus tutus . Sp. nov.
Plate XI View PLATE XI , plate XII, figs. 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5 View PLATE XII , and plate XXI, figs. 6, 7 and 8 View PLATE XXI View PLATE XXI .
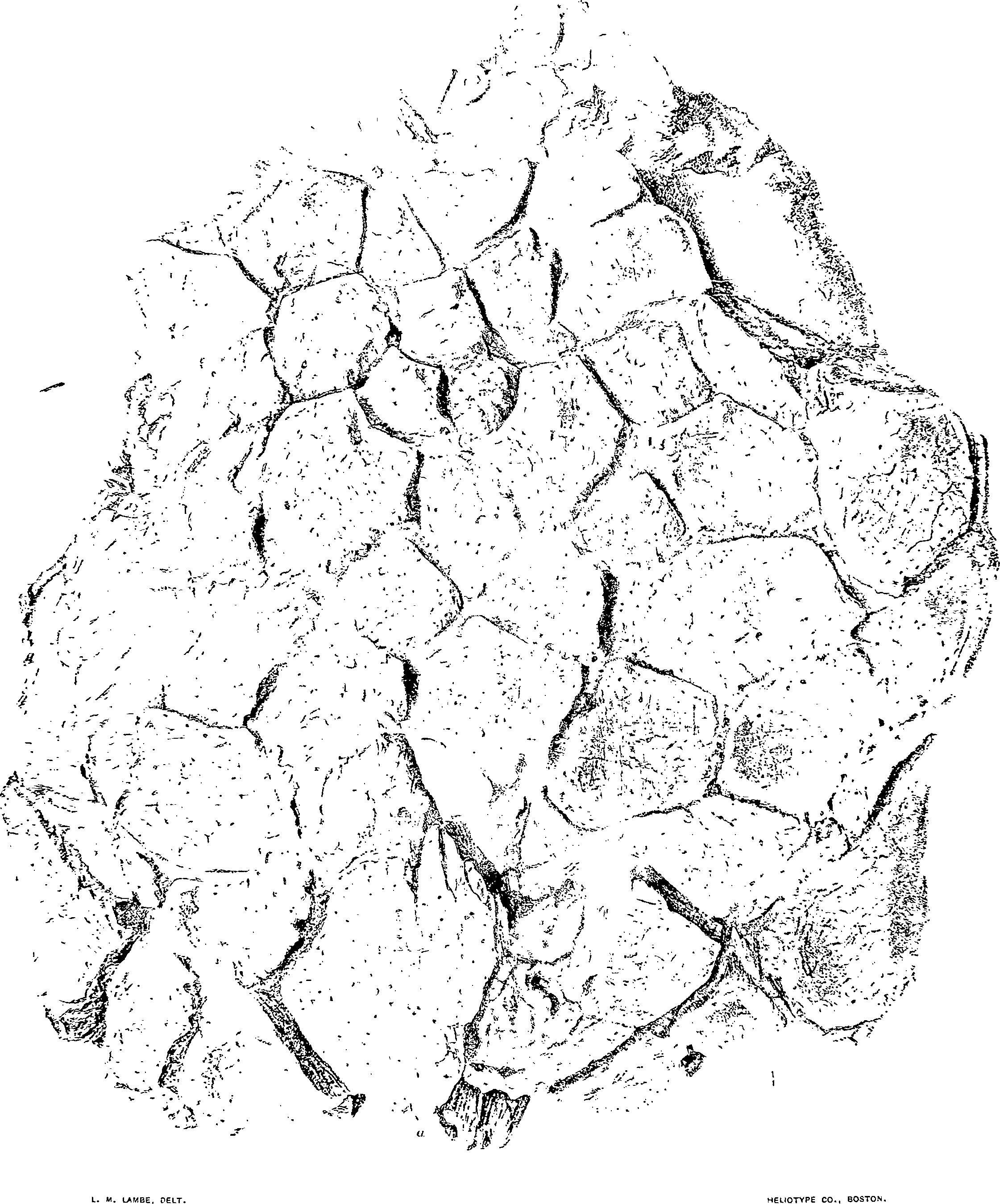
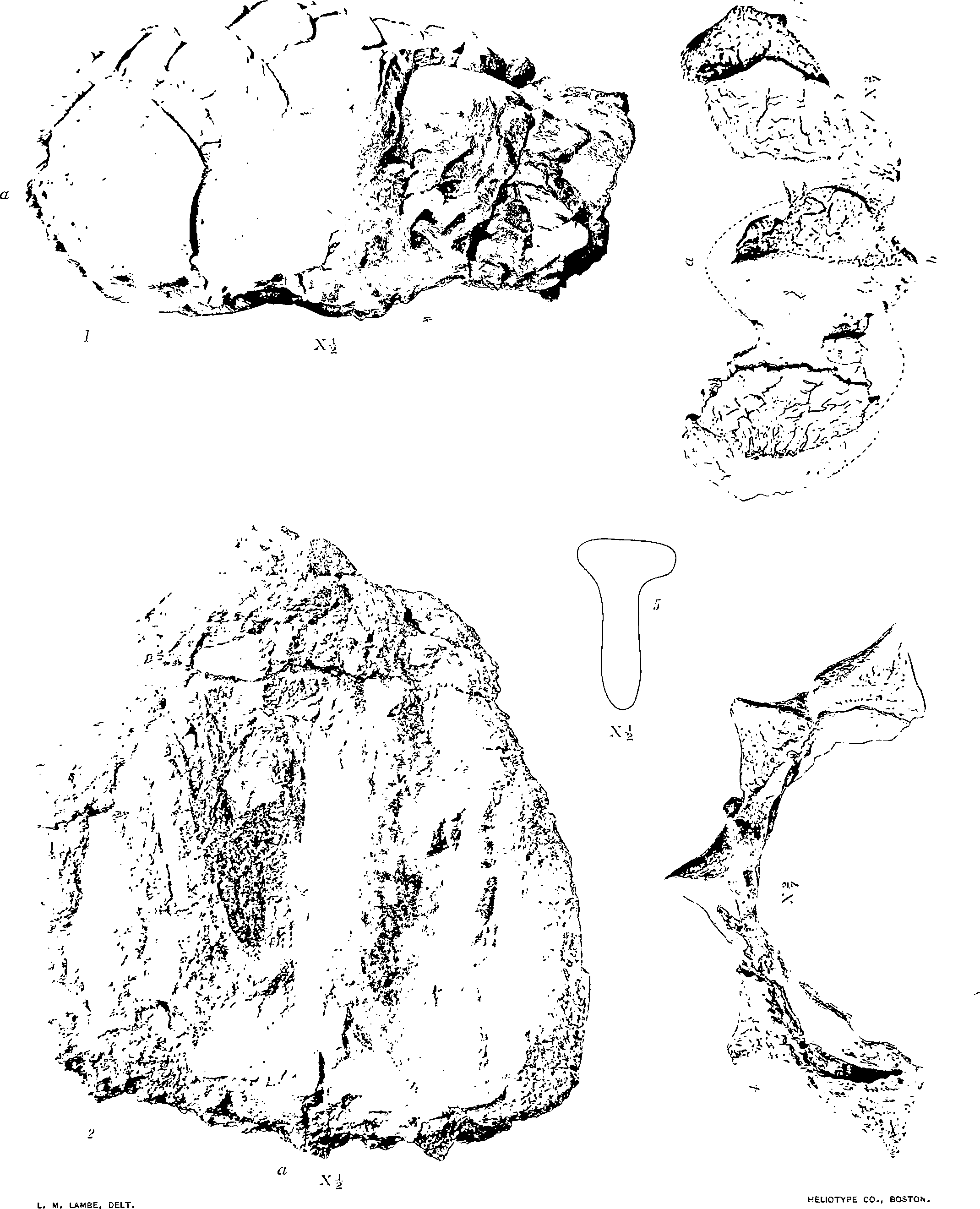
The speeimen of Which views from above, from the side and from below are given on plates XI and XII, represents part of the plate-protected cranium of a herbivorous dinosaur, that is, apparently, quite distinct from any hitherto described.
With the head was found a transverse series of coössified sharply keeled scutes which will be described farther on.
The part of the head preserved is strongly convex transversely, but only moderately so from front to back. Goôssified plates cover the whole of the upper surface and are continued down on the vertical sides. They are arranged with a certain amount of bilateral symmetry, are quite small at the centre and toward the back, but are larger in front and very much more so on the sides. They are for the most part irregularly five or six sided, with rather undulatory surfaces that are marked by an irregular, raised, structural cross-hatching, feebly suggestive of the surface markings of the plates of Nodosaurus textilis, Marsh. Small vascular openings and grooves are also numerous on the surface. The edges of the plates are as a rule angular and sometimes raised. Each plate has its limit defined by a deep circumscribing furrow, so that although they are coôssified and form a continuous surface covering to the head, they do not lose their individuality. A rounded node, or an incipient keel is noticed on some of the plates.
The removal of sandstone from the lower surface of the specimen revealed the bones of the palatal region ( plate XII View PLATE XII . fig. 2). The interpretation of these elements are as indicated by the letters. The back ends, only, of the palatines (P) are seen, meeting the pterygoids in a suture indicated at “ s. From here the latter bones (pt.) extend backward on either side of interpterygoid vacuities (v.). The ridge (pb.) represents the presphenoid and basisphenoid elements; it is bent posteriorly to one side in the specimen, which has been subjected to considerable pressure from above and is somewhat crushed behind.
From this intel'pretation of the bones of the palate it would appear that the part of the armature preserved covers the upper part of the head near the union of the nasals With the frontals. No indication of the 01'bits can be detected and it is probable that they were placed far forward in the head.
| Ãfeasurevnents. | ||
|---|---|---|
| M. | ||
| Antero-posterior diameter of speeimen. | ‘ 250 | |
| Greatest transverse diameter. | ' 210 | |
| Height of centre of upper surface above the level. | 1225 | |
| \Vidth of interpterygoid vacuities K' | about. | ‘ 040 |
| Maximum thickness of cranial armature. | . about about | ' 016 |
| fllezısurenıents of transverse series of scutes. | |
|---|---|
| M | |
| Height of apex of median keel above the level. | 190 |
| Height of centre of inner surface of arch above the level. | 125 |
| Width of inner spread of arch below | ' 236 |
| Average height of apices of keels above inner surface of arcli | ' 072 |
| Basal breadth of the seutes (Nos. 2 and 4) on either sidc of the median one. | ' 075 |
| 'Basal length of same. | 143 |
| Thickness of bone on which the scutes rest, about. | ' 010 |
Belly River series, Red Deer river, 1897.
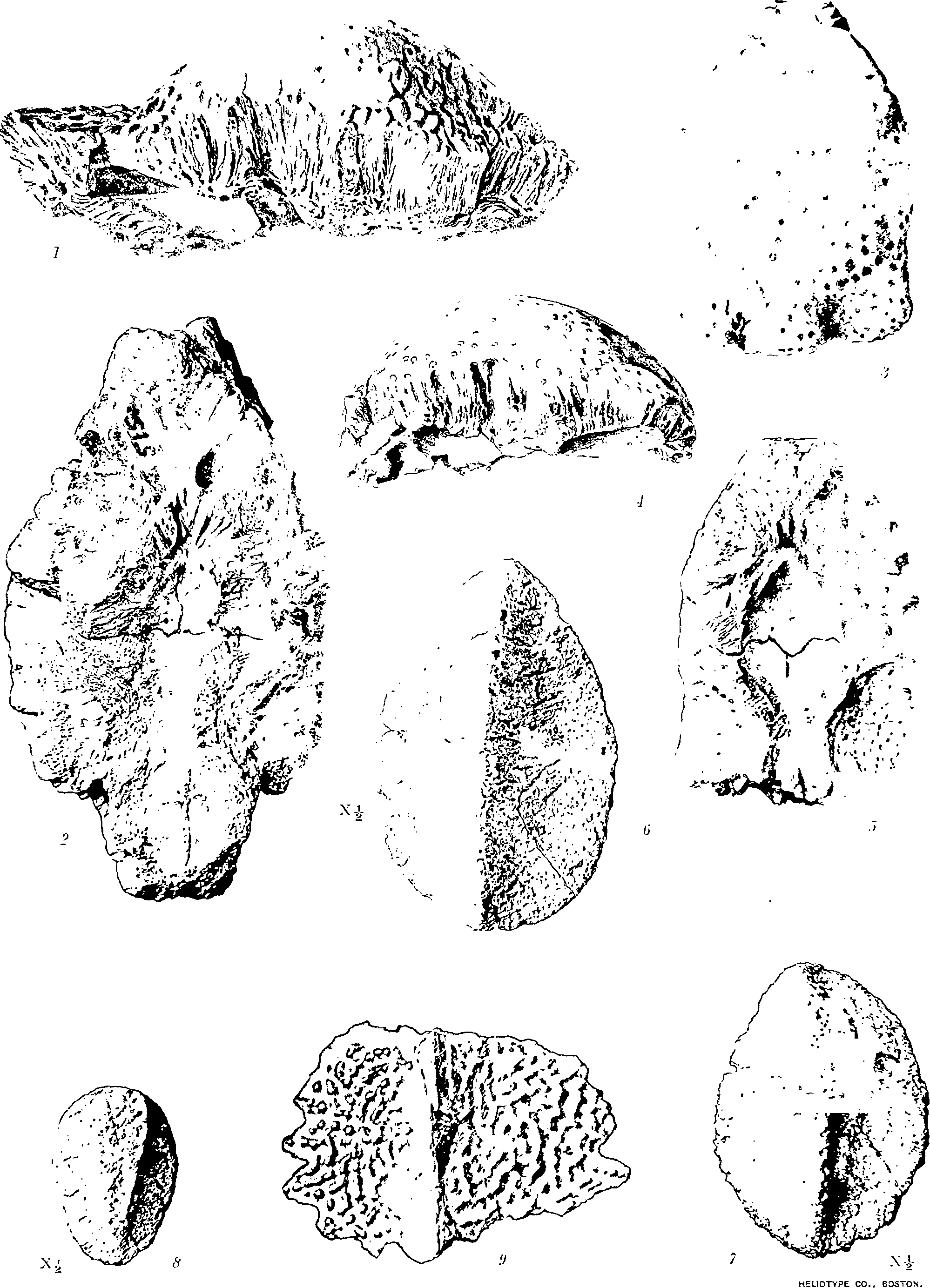
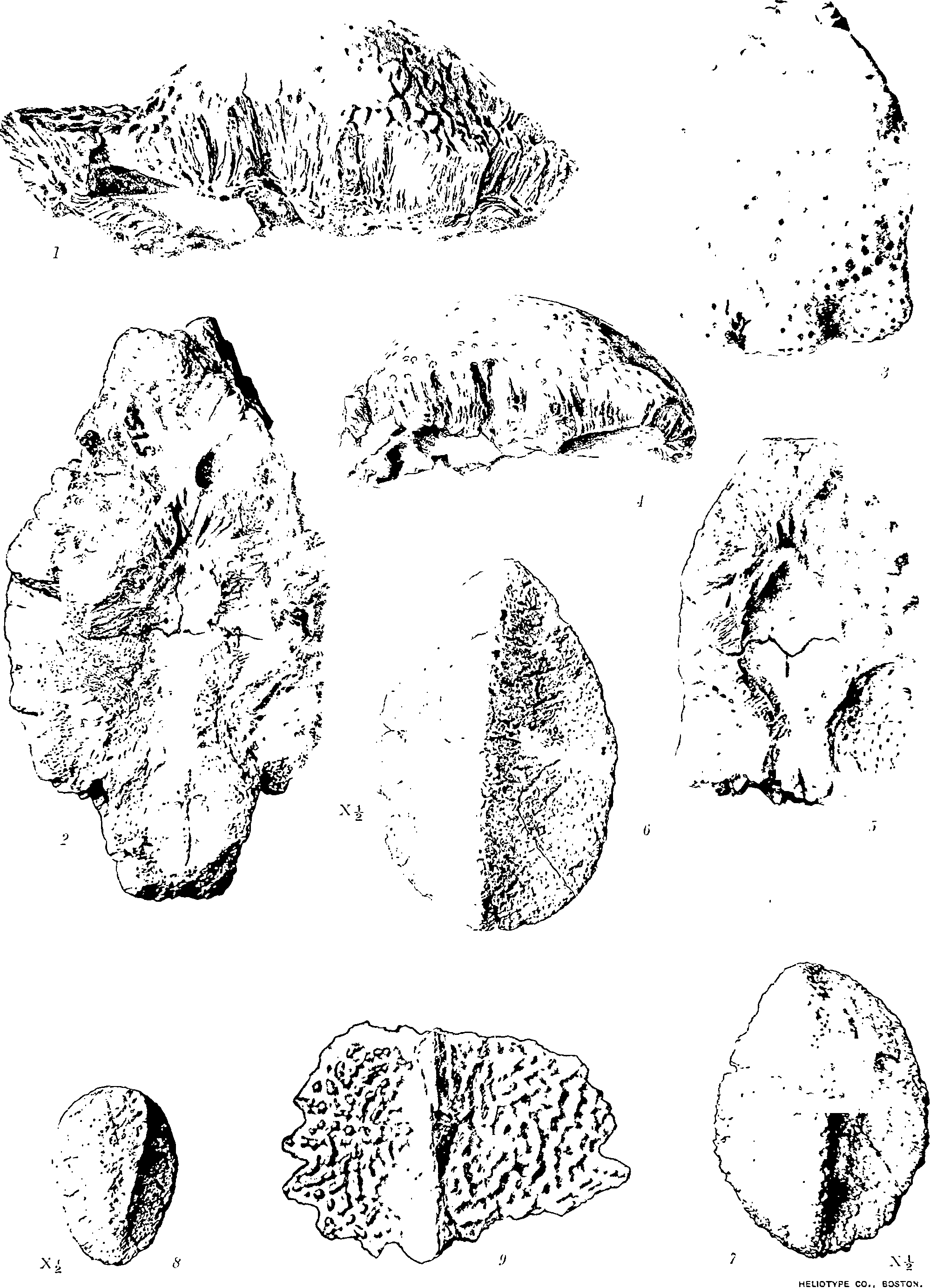
The tooth shown in fig. 12, is of the Stegosaurían type. It differs from those, of the Red Deer river district, referred to the two species of Palœoscincus, and is about twice as large as those of P. costatus. 1 t is figured here with the idea that it may eventually prove to belong to S. tutus. It was collected below Berry creek, on Red Deer river, in 1901.
A spinous dermal plate of massive proportions, fig. 13, A and B, is referred to this species on account of its similarity, in structure and surface markings, to the postcranial keeled scutes described above. This specimen was collected in 1897. Another large plate similar in general proportions to the above and nearly as large, as Well as numerous others of different sizes and of a variety of shapes, were collected in 1901.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Stereocephalus tutus
| Lambe L. M. 1902 |
S. tutus
| Lambe 1902 |